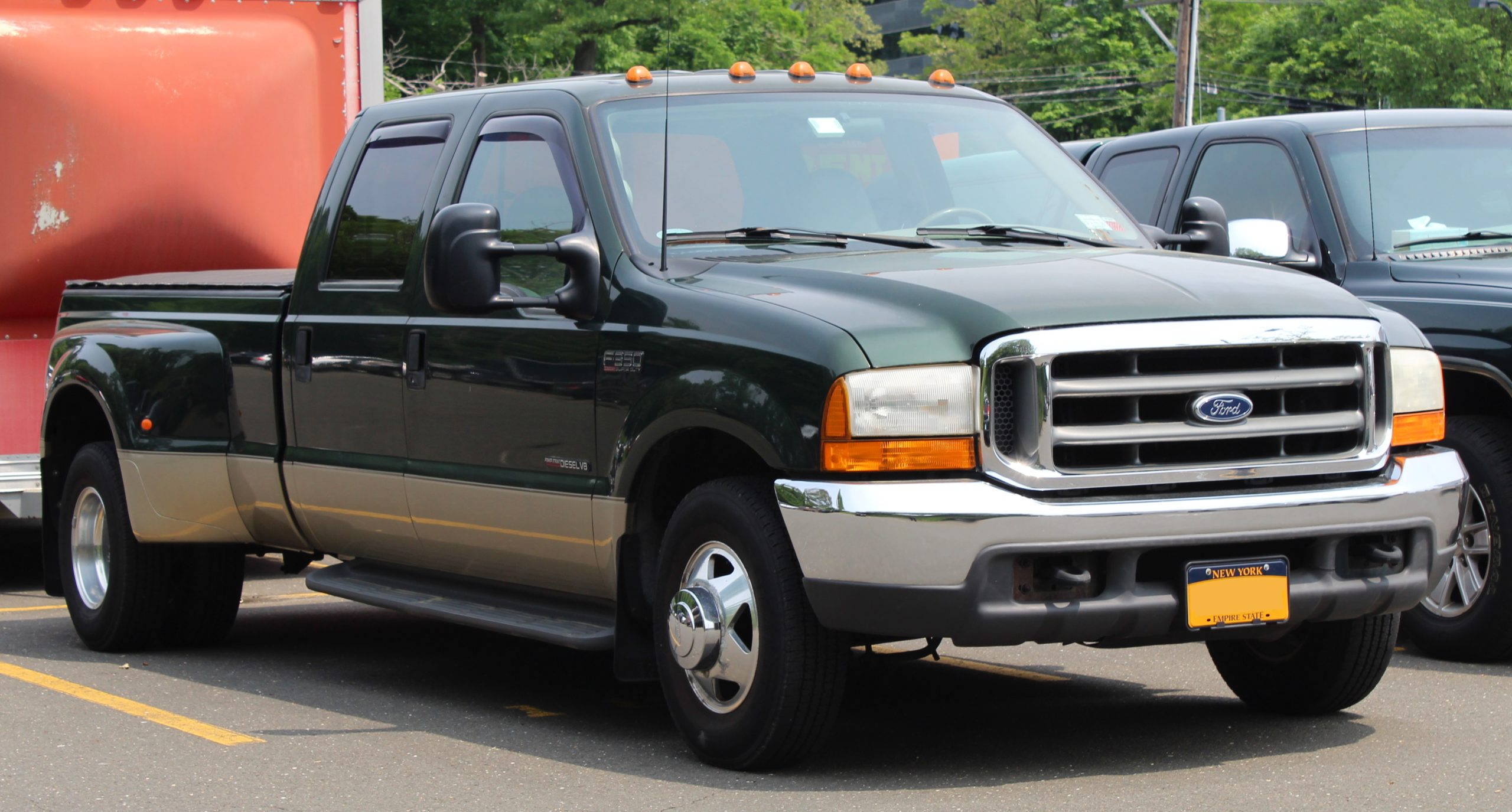
Welcome to the world of the 7.3 Powerstroke engine, a powerhouse known for its performance and reliability. However, not all years of this iconic engine are created equal.
In this guide, we will delve into the issue of 7.3 Powerstroke years to avoid, shedding light on the specific years that have garnered a reputation for troublesome issues and potential pitfalls.
1994 7.3 Powerstroke was the first year of the engine, and it had a few teething problems. The fuel injectors were particularly troublesome, and there were also some issues with the head gasket.
The 2001-2003 7.3 Powerstrokes had a number of problems with the camshaft position sensor (CPS). The CPS is a critical sensor that tells the engine when to fire the spark plugs, and a bad CPS can cause a variety of problems, including stalling, misfires, and poor fuel economy.
I personally owned a 2002 7.3 Powerstroke, and I can attest to the problems with the CPS. I had to replace the CPS twice in the four years that I owned the truck.
If you’re looking for a 7.3 Powerstroke, I would avoid the years 1994, 2001-2003. There are plenty of other good years to choose from, such as 1998-2000.
Overview of 7.3 Powerstroke

Here are some of my personal thoughts and experiences with the 7.3 Powerstroke:
- I love the power and torque of the 7.3 Powerstroke. It’s a great engine for towing and hauling.
- I’ve been very impressed with the reliability of the 7.3 Powerstroke. I’ve never had any major problems with my truck.
- The 7.3 Powerstroke is a relatively simple engine, which makes it easy to maintain and repair.
Overall, I’m very happy with my 7.3 Powerstroke. It’s a great engine that’s been very reliable for me. I would definitely recommend it to anyone who’s looking for a powerful and durable diesel truck.
7.3 Powerstroke Engines History
The 7.3 Powerstroke engine is a V8 diesel engine that was produced by Ford from 1994 to 2003. It was based on the Navistar T444E engine and was offered in three-quarter-ton and larger versions of the Ford F-Series and Econoline product ranges.
The 7.3 Powerstroke was a direct injection (DI) engine, which meant that fuel was injected directly into the combustion chamber. This design improved the efficiency of the engine’s fuel system and power output and also helped to reduce emissions.
The 7.3 Powerstroke was available in two different power outputs: 210 horsepower and 420 lb-ft of torque, or 275 horsepower and 500 lb-ft of torque. It was paired with a four-speed automatic transmission.
The 7.3 Powerstroke was known for its reliability. It was one of the most reliable diesel engines on the market and was often praised by owners and mechanics. The engine was also relatively easy to maintain, and parts were readily available.
The 7.3 Powerstroke was discontinued in 2003 and was replaced by the 6.0 Powerstroke engine. However, the 7.3 Powerstroke remains a popular engine among Ford truck enthusiasts. It is often sought after for its reliability and performance and is still considered to be one of the best diesel engines ever produced.
Here are some of the reasons why the 7.3 Powerstroke is so reliable:
- It is a simple engine with few moving parts.
- It uses a cast-iron block and head, which are both very durable.
- The engine is designed to run on low-sulfur diesel fuel, which helps to reduce emissions and extend the life of the engine.
- The engine has a reputation for being easy to maintain and repair.
If you are looking for a reliable diesel truck, the 7.3 Powerstroke is a great option. It is a powerful and efficient engine that will last for many years with proper maintenance.
7.3 Powerstroke Life Expectancy

The 7.3 Powerstroke engine is a very reliable engine that can last for many years with proper maintenance. The average life expectancy of a 7.3 Powerstroke engine is 400,000 to 500,000 miles. However, there are many examples of 7.3 engines that have surpassed 600,000 miles.
Here are some tips for extending the life of your 7.3 Powerstroke engine:
- Change the oil and filter regularly.
- Use high-quality diesel fuel.
- Inspect the engine regularly for fuel filter housing leaks or other signs of wear.
- Have the engine tuned up regularly.
- Avoid overloading the truck.
- Drive the truck at a moderate speed.
By following these tips, you can help ensure that your 7.3 engine will last for many years to come.
Common 7.3 Powerstroke Engine Problems
While the 7.3 Powerstroke engine is renowned for its durability and longevity, it’s not without its share of potential issues. Here are some common problems that owners might encounter:
1. Injector Failures
One of the most common issues with the 7.3 Powerstroke is injector failures. These can lead to poor engine performance, misfires, and even engine damage if not addressed promptly.
2. Camshaft Position Sensor (CPS) Failure
The CPS in the 7.3 Powerstroke can occasionally fail, leading to engine stalling or hard starts. However, it’s usually a straightforward fix, and many owners keep a spare sensor on hand just in case.
3. Glow Plug Problems
The 7.3 Powerstroke relies on glow plugs for cold-start situations. Over time, these can fail, leading to hard starts in cold weather. Regular checks can help prevent unexpected failures.
4. Oil Leaks
Oil leaks, particularly from the oil cooler and turbo pedestal, are not uncommon. While these fuel leaks don’t typically affect performance, they can lead to a messy engine bay and should be addressed to prevent further complications.
5. Transmission Issues
Automatic transmission issues are also reported in some older Ford engines. Regular maintenance and fluid changes can significantly prolong the transmission life.
Despite these potential problems, the 7.3 Powerstroke remains a beloved workhorse. Like any engine, regular maintenance and prompt attention to issues will ensure it continues to run strongly for hundreds of thousands of miles.
Powerstroke Turbo Failure Symptoms
Here are some of the symptoms of a Powerstroke turbo failure in a few words:
- Loss of power
- Whistling noise
- Exhaust smoke
- Engine overheating
- Oil leaks
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to have your truck checked by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible. A failing turbo can cause serious damage to your engine, so it is important to get it repaired as soon as possible.
Should You Buy a 7.3 Powerstroke Engine?
The 7.3 Powerstroke engine, known for its outstanding durability, longevity, and performance, can be a solid investment for those seeking a reliable and powerful diesel engine.
Despite potential maintenance and repair needs, it’s an engine that has stood the test of time, often delivering hundreds of thousands of miles of service.
If your driving needs involve heavy-duty tasks like towing or hauling, or if you simply appreciate a robust and high-performing engine, the 7.3 Powerstroke could be an excellent choice.
As always, it’s crucial to consider your individual needs and circumstances when making this decision.
FAQ’s
What Is The Best 7.3 Powerstroke Year?
The best year for the 7.3 Powerstroke engine is generally considered to be 1999 or 2000. These years saw the introduction of several new features that improved the performance and reliability of the engine, including a new air-to-air intercooler, higher-flowing injectors, and a new 4R100 automatic transmission.
7.3 Powerstroke Years To Avoid and Why?
While the 7.3 Powerstroke is generally reliable, the earlier production years from 1994 to 1997 had some limitations. They offered lower horsepower and torque and lacked an intercooler, which improved performance in later models.
However, a well-maintained engine from these years can still be a dependable choice. Always consider the vehicle’s specific maintenance and usage history rather than focusing solely on the model year.
Is 7.3L Better than 6.0L Powerstroke?
The 7.3L Powerstroke is generally considered to be a better engine than the 6.0L Powerstroke. It is more reliable, easier to maintain and repair, and gets better fuel economy. However, it does not have as much power or torque as the 6.0L Powerstroke.
The valve springs and valve cover harness in the 7.3 engine are crucial components for smooth operation and electrical connectivity. The exhaust back pressure valve helps in optimizing performance and emissions control.
Ultimately, the decision of which engine is better for you depends on your individual needs and preferences. If you are looking for a reliable engine that is easy to maintain and repair, the 7.3L Powerstroke is the better option. If you are looking for an engine with more power and torque, the 6.0L Powerstroke is the better option.
Final Thoughts
I’ve owned a 7.3 Powerstroke for about 10 years now, and I’ve loved every minute of it. It’s a reliable, powerful, and easy-to-maintain engine. However, there are a few years that I would recommend avoiding.
The 1994 model year is known to have problems with the head gasket. The gasket is not thick enough and can crack, which can lead to coolant leaks and engine damage. The 2001-2003 models are known to have problems with the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). The bug can cause the engine to stall or run rough.
If you are considering buying a 7.3 Powerstroke, I would recommend avoiding these years. If you do buy a truck from one of these years, be sure to have it inspected by a qualified mechanic before you buy it.
Personally, I’m glad that I didn’t buy a 7.3 Powerstroke from one of these years. I’ve had no problems with my truck, and I’ve been able to keep it running smoothly with regular maintenance.
If you’re looking for a reliable and powerful diesel truck, the 7.3 Powerstroke is a great option. Just be sure to avoid the 1994 and 2001-2003 model years.
Moreover, you can also find helpful information on what year 6.7 powerstroke to avoid in order to steer clear of any risky decision!

